Many businesses today, especially in fields such as medical, automotive or aerospace, will not purchase inadequately marked products from suppliers as verification and quality are imperative. The systems used in marking include a wide variety of marking tools which emboss, engrave, etch, stamp or otherwise create designs on surfaces of metals, glass, plastics, marble, paper and other materials. Read More…
Epilog Laser specializes in laser marking systems, CO2 lasers, diode lasers, laser cutting machines & systems for laser engraving like tabletop engravers, mid-sized engravers & large-format engraving systems. We have offered laser technology since 1988 and are the leader in CO2 & fiber laser systems.

Is your facility in need of high performance dot peen machines? Our top of the line machinery is guaranteed to meet all of your needs. We are your worry-free provider of identification systems. We will work with your team to implement our products into your business and our services are beyond compare. Our company has proven ourselves as an industry leader!

Laser Marking Technologies LLC has served the marking machinery and laser cutting services industries for over 20 years. Our years of experience and advanced technology make us a leader in marking machinery and laser-cutting services.

At Automark, our team of experts is ready and willing to tackle any of your challenging assignments. We supply marking systems for a multitude of industries such as medical, cosmetic, industrial, automotive, and more. All of our machines are manufactured to the highest quality, offered at a competitive price, and are guaranteed to last. Give us a call and a representative will speak with you...

Isotech offers a full range of Fiber, C02, UV, Green, MOPA, Nanosecond, Picosecond and Femtosecond laser systems for marking, cutting and welding of many substrates. Isotech offers both standard systems as well as fully automated or custom systems depending on your specific requirements. Integrated, automated solutions with conveyors, palletized pick and place, rotary dial tables, hoppers, and...

More Marking System Manufacturers
Industrial Marking Techniques: Processes, Applications, and Selection Guide
Industrial marking is essential for product identification, traceability, branding, and regulatory compliance across diverse sectors. Today’s manufacturers rely on a wide range of marking methods—including laser marking, press marking, roll marking, stylus marking, and nameplate marking—to meet demanding specifications for permanence, precision, and efficiency. Understanding the advantages, use cases, and decision factors behind each marking technology is key for optimizing production workflows and ensuring the longevity and clarity of permanently applied marks.
Overview of Industrial Marking Methods
There are several primary techniques used for industrial part marking, each with unique benefits, limitations, and ideal applications. The most widespread marking systems include:
- Laser Marking: Uses focused laser beams to produce high-contrast, permanent marks on various materials. Laser marking is prized for its speed, flexibility, and ability to create fine detail without physical contact.
- Press Marking: Employs a hydraulic ram or press to physically indent a mark or imprint into the surface of a component. It is suitable for robust parts that can withstand significant force.
- Roll Marking: Involves the use of rollers or type holders that press a design into round or flat surfaces, ideal for cylindrical or tube-shaped parts.
- Stylus Marking: Utilizes a rapidly oscillating or dragged stylus to distort the material’s surface, generating images or alphanumeric codes. It’s highly versatile for variable data or graphics.
- Nameplate Marking: Engraves or prints information on metal or plastic nameplates, often used for equipment identification, asset tracking, and compliance labeling.
- Embossing: Raises or recesses portions of the material to create tactile, durable marks, commonly used for branding or decorative applications.
Choosing the right marking process depends on several key factors, including the material type and its hardness, the desired mark durability, required resolution, production throughput, and integration with existing manufacturing systems.
How to Choose the Right Marking System for Your Application
With so many marking options, how do you select the best solution for your specific needs? Consider the following decision criteria to guide your evaluation process:
- Material Compatibility: What type of substrate are you marking—metal, plastic, ceramic, glass, coated or uncoated surfaces? Different marking systems excel with different materials.
- Mark Permanence: Is long-term readability essential, even in harsh or outdoor environments? If so, permanent marking methods such as laser engraving or embossing may be optimal.
- Precision and Detail: For intricate logos, barcodes, or serial numbers, technologies like laser marking offer the highest resolution.
- Production Volume: Are you marking high volumes at high speed, or do you require flexible, low-volume or batch processing?
- Automation and Integration: Does the marking process need to be integrated into automated production lines, or is manual operation sufficient?
- Cost and ROI: Consider the initial investment, ongoing maintenance, and consumables cost for each marking technology.
- Regulatory and Industry Standards: Are there compliance requirements (such as UID, CE, or ISO standards) governing your marking process?
Not sure which marking method is right for your industry or application? Explore our in-depth FAQ section below for answers to common search queries such as:
- What is the difference between laser marking and engraving?
- How do I choose a marking system for medical device traceability?
- Can I mark both metal and plastic parts with the same machine?
- What are best practices for permanent industrial part marking?
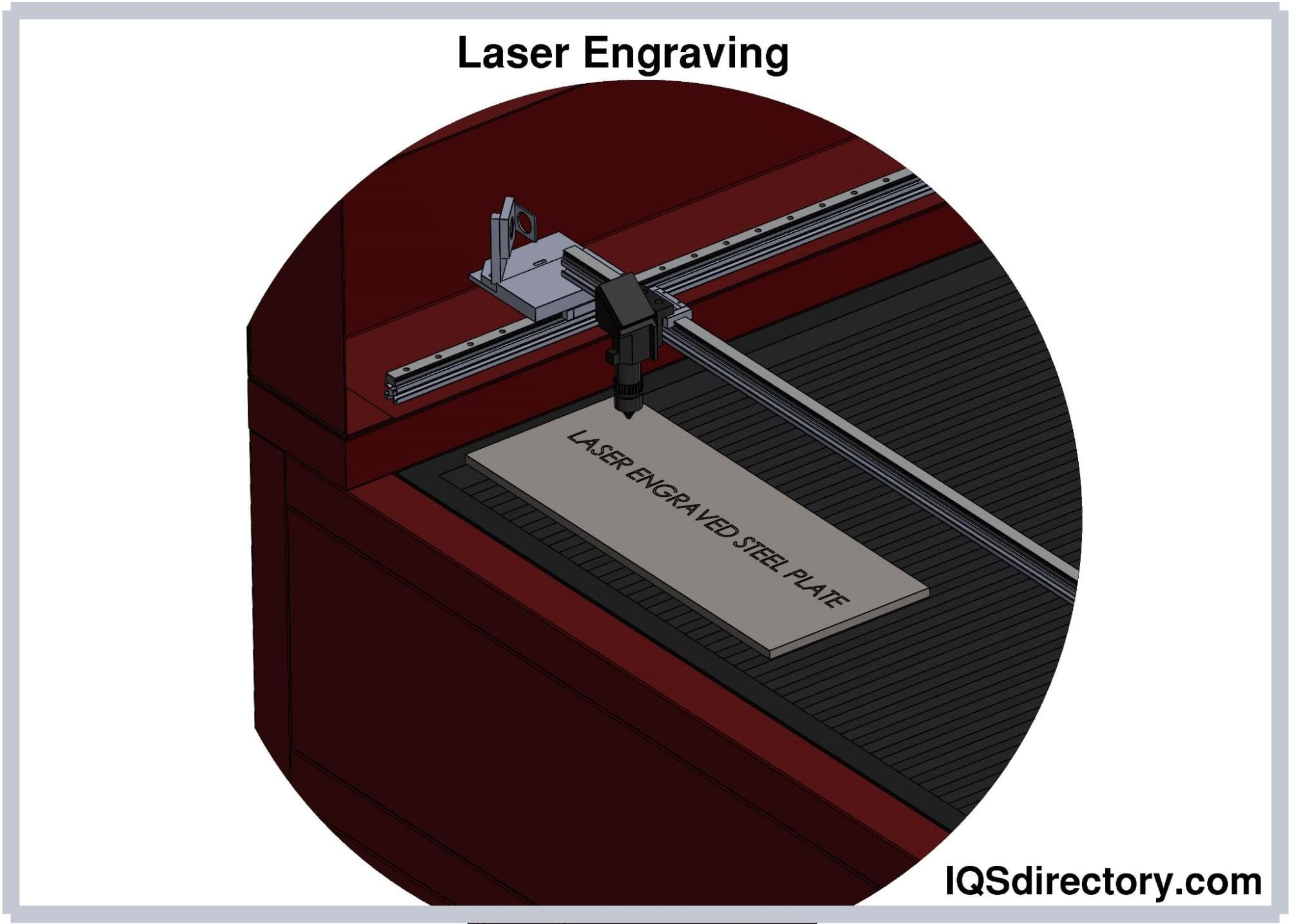
Laser Marking: The Modern Standard for Permanent Marks
Laser marking has become the industry standard for many manufacturers seeking fast, precise, and non-contact identification solutions. This method uses high-powered lasers—such as fiber lasers, CO2 lasers, and UV lasers—to create a variety of marks, including:
- Annealing: Alters the color of the metal surface without removing material—ideal for medical devices, surgical instruments, and stainless steel parts where corrosion resistance must be preserved.
- Etching: Uses laser energy to vaporize the surface, creating high-contrast marks on metals, plastics, ceramics, and more.
- Engraving: Removes more material to create deep, lasting marks that withstand wear, abrasion, or chemical exposure.
- Foaming: Generates raised marks, particularly on plastics, by causing localized melting and bubbling.
- Color Change: Alters the chemical structure of the material to produce visually distinct marks, especially on polymers.
Laser marking systems are favored in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical device manufacturing, electronics, and defense due to their versatility, speed, and ability to meet strict quality standards. Advanced laser marking machines can be programmed for fully automated, high-throughput production, or operated as standalone workstations for prototyping and custom jobs.
Key Benefits of Laser Marking
- Contact-free process reduces risk of part deformation or contamination
- Fine detail, high resolution, and consistent accuracy for barcodes, QR codes, serial numbers, and logos
- Works on metals, plastics, ceramics, glass, and coated materials
- Low operating cost—no consumables, minimal maintenance
- Environmentally friendly—no inks or chemicals needed
- Permanent, tamper-resistant marks suitable for compliance and traceability
Want to learn more about the differences between laser marking, laser engraving, and laser etching? See our full guide to laser marking machines.
Press Marking: Durable Indentation for Industrial Components
Press marking remains a popular choice for creating indented marks on hard, durable materials—especially metals. Using a hydraulic or mechanical press, the process impresses a die or stamp into the workpiece, forming a permanent, legible mark. Typical applications include:
- Automotive parts (e.g., VIN numbers, engine blocks)
- Steel bars, tubes, and pipes
- Large industrial castings and forgings
- Heavy machinery components
Since press marking is a high-force process, it’s best suited for robust materials and is not recommended for delicate, thin, or brittle substrates. Press marking machines are available in manual, semi-automatic, and fully automated configurations to suit both small job shops and large-scale manufacturing lines.
Advantages of Press Marking
- Creates deep, permanent imprints resistant to wear
- Simple, reliable operation with minimal setup
- Suitable for flat or slightly curved surfaces
- Low equipment cost compared to advanced laser systems
Roll Marking: Efficient Marking for Cylindrical and Round Parts
Roll marking is specifically designed to apply marks to cylindrical, tubular, or flat parts using rolling dies or type holders. By rotating the part or die against each other under pressure, roll marking can quickly imprint serial numbers, logos, or graduations onto large batches of components. Common use cases include:
- Pipe and tube manufacturers
- Axles, shafts, and rods
- Bearing housings and bushings
- Wiring and cable marking
Roll marking is valued for its high throughput and ability to produce uniform marks on round or curved surfaces, making it a staple in industries requiring fast, repeatable marking for mass production.
Roll Marking Benefits
- High-speed operation for continuous, automated lines
- Consistent mark quality for repeat parts
- Adaptable to various diameters and shapes
Stylus Marking: Flexible, Programmable Dot Peen Marking
Stylus marking, also known as dot peen marking, is a method where a pneumatically or electrically actuated stylus rapidly indents or drags across the surface to form characters, codes, or images. The stylus can be programmed to create both simple text and complex graphics, making it ideal for:
- Batch coding and serialization
- Custom logos or data matrix codes
- Marking both soft and hard metals, some plastics, and coated surfaces
- Automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication industries
Stylus marking machines are available as handheld devices for marking large or immobile parts, as well as integrated systems for automated production lines. They offer flexibility for a wide range of marking tasks, including variable data marking, part traceability, and more.
Why Choose Stylus Marking?
- Programmable for unique or variable data
- Works on flat, curved, and irregular surfaces
- Minimal consumables and low running costs
- Durable marks that withstand harsh environments
Nameplate and Embossing Marking: Specialty and Compliance Solutions
Nameplate marking involves engraving or printing on metal or plastic plates, which are then affixed to products, equipment, or machinery. These nameplates provide vital information such as asset numbers, certification data, safety warnings, and branding. Industries like electrical, HVAC, manufacturing, and utilities rely on nameplate marking for regulatory compliance and asset management.
Embossing machines (learn more) are used to create raised or recessed designs, adding tactile, wear-resistant marks to metals, plastics, or paper. Embossed marks are often used for:
- Brand identification on consumer products
- Decorative finishes for packaging and promotional items
- Credit card and ID card personalization
- Industrial tags and labels requiring long-term durability
Advantages of Nameplate and Embossing Marking
- Highly legible, durable information display
- Wide range of materials and customization options
- Resistant to environmental factors such as chemicals, abrasion, and UV exposure
Applications: Where Are Marking Systems Used?
Marking systems are critical across numerous industries for ensuring product traceability, safety, and compliance with global standards. Common applications include:
- Automotive manufacturing: VIN numbers, component serial numbers, quality control marks
- Aerospace and defense: Part identification, lot codes, manufacturer information
- Medical devices: Unique Device Identification (UDI) codes, surgical instrument tracking, implant traceability
- Electronics: PCB marking, component coding, anti-counterfeiting
- Oil & gas: Pipe and valve identification, compliance labels
- Consumer goods: Brand logos, warranty marks, batch codes
- Industrial equipment: Asset tags, safety labels, maintenance records
- Packaging: Lot codes, expiration dates, regulatory information
Frequently Asked Questions About Industrial Marking
What is the difference between laser marking, engraving, and etching?
While all three use a laser, laser marking generally refers to any process that leaves a mark by changing the surface properties of a material. Laser engraving removes material to form a deep, permanent mark, while laser etching vaporizes the top layer to create a shallow, high-contrast mark. Learn more in our complete guide to laser marking.
How do I choose the right marking system for my production environment?
Assess your substrate material, required mark permanence, production speed, integration needs, and budget. Consider regulatory requirements specific to your industry. Use our Marking System Selection Guide above for a detailed comparison of marking technologies.
Can a single marking machine handle multiple materials?
Many modern marking systems—especially laser and stylus markers—can process a variety of materials (metals, plastics, ceramics, composites). However, optimal results may require adjusting laser wavelengths, marking parameters, or tooling for each material type.
What industries benefit most from advanced marking solutions?
Industries with strict traceability and compliance needs—such as aerospace, automotive, medical device, electronics, and defense—see the greatest benefits. However, any sector requiring durable product ID, branding, or regulatory information will benefit from high-quality marking systems.
What are the cost considerations for industrial marking equipment?
Initial investment varies by technology: laser marking systems tend to have higher upfront costs but lower ongoing expenses, while press and roll marking equipment is more affordable but may require more maintenance. Factor in consumables, downtime, and productivity gains to calculate ROI.
Is permanent part marking required by law?
Many industries are governed by regulations (such as UDI for medical devices, automotive VIN requirements, or aerospace part traceability standards) that mandate permanent, legible marks. Check your industry’s regulatory guidelines for specific marking requirements.
What are best practices for ensuring mark quality and longevity?
Select the appropriate marking method for your substrate and application. Regularly calibrate and maintain equipment. Test marks under expected environmental conditions, and document marking parameters for consistency. Consider post-marking treatments to enhance durability if required.
Ready to Find the Ideal Marking Solution?
Choosing the right industrial marking system is a critical decision that can impact product quality, traceability, and compliance for years to come. Whether you’re looking to upgrade to state-of-the-art laser marking technology, expand your capabilities with flexible stylus or roll marking, or ensure regulatory compliance through robust nameplate and embossing solutions, our experts can help you evaluate the best options for your unique requirements.
Still have questions? Contact us for a personalized assessment or browse our directory of leading marking machinery manufacturers to request a quote, schedule a demo, or download technical specifications.
Explore More Resources
- Laser Marking Machines: Complete Buyer's Guide
- Embossing Machines Overview and Applications
- Compare Top Marking Machinery Suppliers
- Industrial Marking FAQ: Get Answers to Common Questions
Optimize your marking processes for efficiency, compliance, and long-term value—discover the marking technology that best fits your business needs today.








 Cardboard Tubes
Cardboard Tubes Carrying Cases
Carrying Cases Contract Packaging
Contract Packaging Corrugated Boxes
Corrugated Boxes Dot Peening Machines
Dot Peening Machines Labeling Machinery
Labeling Machinery Marking Machinery
Marking Machinery Packaging Equipment
Packaging Equipment Palletizers
Palletizers Plastic Bags
Plastic Bags Sewing Contractors
Sewing Contractors Tape Suppliers
Tape Suppliers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services