Marking machinery is any machinery or tool used to create markings on parts and products. Markings such as these include designs, images, logos, identification codes, and more. Part marking has a wide range of applications. First, it can be used to value products, maintain quality control, deter counterfeiting, ease the returning of products, and create increased customer recognition. Read More…
Epilog Laser specializes in laser marking systems, CO2 lasers, diode lasers, laser cutting machines & systems for laser engraving like tabletop engravers, mid-sized engravers & large-format engraving systems. We have offered laser technology since 1988 and are the leader in CO2 & fiber laser systems.

Is your facility in need of high performance dot peen machines? Our top of the line machinery is guaranteed to meet all of your needs. We are your worry-free provider of identification systems. We will work with your team to implement our products into your business and our services are beyond compare. Our company has proven ourselves as an industry leader!

Laser Marking Technologies LLC has served the marking machinery and laser cutting services industries for over 20 years. Our years of experience and advanced technology make us a leader in marking machinery and laser-cutting services.

At Automark, our team of experts is ready and willing to tackle any of your challenging assignments. We supply marking systems for a multitude of industries such as medical, cosmetic, industrial, automotive, and more. All of our machines are manufactured to the highest quality, offered at a competitive price, and are guaranteed to last. Give us a call and a representative will speak with you...

Isotech offers a full range of Fiber, C02, UV, Green, MOPA, Nanosecond, Picosecond and Femtosecond laser systems for marking, cutting and welding of many substrates. Isotech offers both standard systems as well as fully automated or custom systems depending on your specific requirements. Integrated, automated solutions with conveyors, palletized pick and place, rotary dial tables, hoppers, and...

More Marking Machinery Manufacturers
Many everyday items, including credit and debit cards, packaging boxes, and electronic components, are marked by specialized machines. As the need for precise product identification, traceability, and compliance increases, industries like automotive, medical device manufacturing, aerospace, and electronics demand well-marked products from their suppliers. Industrial marking machinery is now essential for ensuring quality control, product authentication, and regulatory compliance across a diverse range of sectors.
Beyond practical uses in industrial production and logistics, marking systems are also popular for decorative and personalization purposes. People often mark jewelry, writing utensils, greeting cards, wood trim, cables, and glass sculptures. Manufacturers employ marking machinery on a wide variety of materials, such as metal, paper, plastic, wood, leather, glass, fabric, and textiles, making marking equipment highly versatile for both commercial and creative applications.
History of Marking Machinery
Humans have been marking items since long before the advent of modern machinery. One of the earliest examples of engraving dates back between 430,000 and 540,000 years ago, seen in a chiseled shell discovered in Indonesia. Following this discovery, the next oldest artifacts found are ostrich shells with engraved bandings, likely created around 60,000 BC, found at the Diepkloof Rock Shelter in South Africa. These shells were likely used by early humans as containers or cups for water. During the Upper Paleolithic period, which spanned from about 50,000 to 10,000 years ago, humans globally began engraving ivory and bone with depictions that reflected their daily lives and cultures.
Around the 1st Millennium BC, humans started metal marking using techniques like lost-wax casting and chasing, allowing for shallow grooves. It was during this period that they also began engraving gemstones for jewelry and decorative purposes.
During the early 1600s, Jacque Callot, a French printmaker, revolutionized the art of etching with his invention of the échoppe, an etching needle distinguished by its slanted oval point. This innovation enabled metalworkers and artists to replicate the bold, swelling lines typically reserved for engraving techniques.
During the 20th century, governments globally aimed to streamline markets and establish uniform standards for labeling machinery. For instance, in 1984, the European Union introduced the CE mark. Short for Conformité Européenne (European Conformity), this mark visibly identifies products and equipment that meet specified standards. Similarly, countries like the United States and Canada developed their own conformity marks, aligning with and adapting the principles of the CE mark.
Since then, marking technologies have advanced significantly. Today, they play a crucial role in creating intricate electronic markings and high-speed product identification. While handcrafted engraving and etching persist for artisan and low-volume work, CNC machinery and automated marking systems largely dominate these tasks due to their precision, speed, and efficiency.
Types of Marking Machinery
Marking systems encompass a wide variety of machines designed to emboss, etch, stamp, or print designs, serial numbers, barcodes, and graphics onto diverse surfaces. These systems utilize a range of advanced techniques and tools, including laser marking machines, press markers, dot peen machines, and nameplate markers. Additionally, they incorporate other specialized equipment such as embossing machines, engraving machines, roll or rotary marking devices, hot stamping machines, numbering machines, and etching machines.
Choosing the right type of marking machinery depends on your application, material type, marking speed, and durability requirements. Review the most common options below to determine the optimal marking technology for your needs:
- Press markers: Also known as mechanical presses, these machines excel at creating rapid, enduring marks. However, they lack flexibility, require considerable setup time, and are unsuitable for hard or fragile materials. They can also pose safety risks if not properly operated.
- Dot peen machines: Alternatively called dot marking or pin marking machines, these utilize a micro-percussion marking system to imprint objects with a series of closely spaced dots. This method employs a tapping pin for fast and precise marking, ensuring minimal stress on the substrate without significant material removal. Dot peen systems are favored for direct part marking (DPM) in automotive, aerospace, and heavy equipment industries.
- Nameplate markers: Aptly named for their purpose, these are tools designed for imprinting or etching nameplates, often in metal. Nameplate marking is crucial in asset identification and regulatory compliance for industrial equipment, electrical panels, and office environments.
- Embossing machines: These utilize heat and pressure to impress a three-dimensional image onto ductile materials such as plastic, leather, or aluminum. This process permanently deforms the material’s surface, imprinting product information such as serial numbers, expiration dates, or branding. Credit cards, for instance, display raised numbers and letters through embossing.
- Engraving machines: Designed to cut intricate grooves, engraving machinery excels on tough materials such as metals and glass, making them ideal for crafting jewelry, plaques, and industrial components requiring permanent identification.
- Roll marking equipment: Employing cylindrical dies that are rolled physically onto the product, roll markers provide a cost-effective alternative for high-speed, repetitive part marking, especially for cylindrical items like pipes, rods, and shafts.
- Hot stamp presses: These involve several key components: a stamping foil, a heated plate, and a metallic stamp or die. In operation, manufacturers heat the metallic stamp using the hot plate, then apply both the stamp and the foil onto the surface of the part intended for marking. Hot stamp marking is widely used in automotive parts, cosmetic packaging, and electronics housings for its durability and vibrant colors.
- Hand stamping: Performed manually, this cost-effective and straightforward process doesn’t require expensive equipment or highly skilled operators. However, it is labor-intensive and can result in inconsistent marks, making it less suited for high-volume or high-precision operations.
- Numbering machines: Specialized marking devices designed to imprint sequential numbers onto papers and products, numbering machines are typically utilized for legal documentation, tickets, and industrial batch tracking.
- Printing machines: Industrial printing machines serve the additional purpose of marking flat surfaces, typically using ink to create marks. These include inkjet printers, flexographic printers, and screen printers, which are ideal for packaging, labels, and mass-produced consumer goods.
- Industrial inkjet printers: Representing a larger-scale iteration of their household and office counterparts, industrial inkjet systems offer high-speed, non-contact marking with variable data printing. These printers are common in food and beverage packaging, pharmaceuticals, and electronics, though their reliance on impermanent inks can pose environmental and fading concerns.
- Pad printing machines: These enable the printing of 2D marks on 3D products by utilizing silicone pads to transfer images from a printing plate onto the product’s surface. Pad printing is commonly used in electronics, toys, promotional items, and medical equipment marking for its ability to print on complex shapes and delicate surfaces.
- Chemical etching: Utilizing corrosive acids or bases, chemical etching selectively removes material from a surface. The process typically includes five key stages: cleaning, masking, marking/scribing, etching, and mask removal. While cost-effective, chemical etching can yield inconsistent results, making it more suitable for less precision-critical applications or materials such as signage and decorative artwork.
- Plasma etching: Falling into two main categories—vacuum and normal-pressure—plasma etching uses gases like oxygen under reduced pressure to activate molding surfaces. While highly effective for surface modification and cleaning, plasma etching is generally used in microelectronics and medical device manufacturing due to its ability to create very fine, controlled marks.
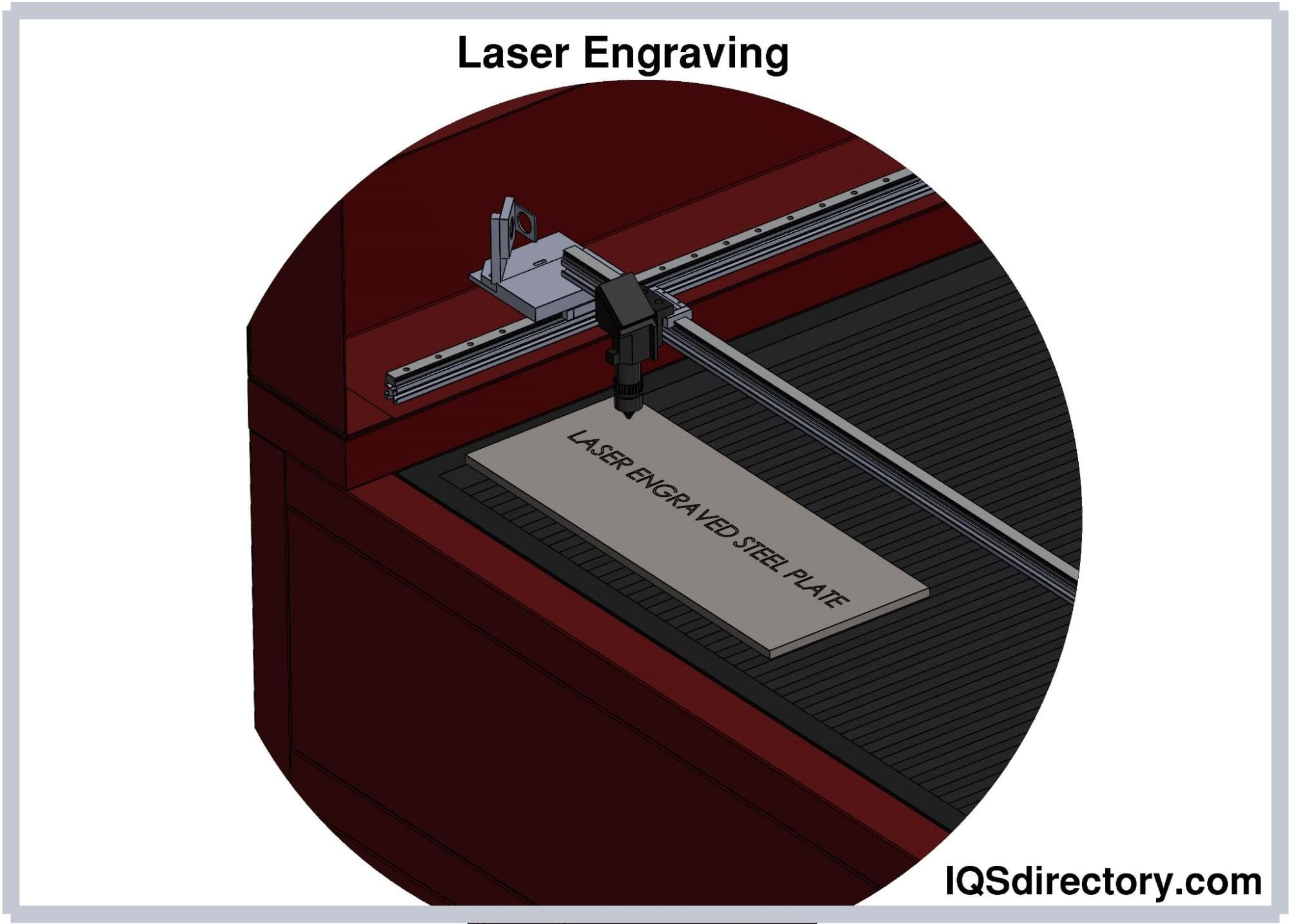
- Laser marking: Leveraging powerful beams of laser radiation, typically from fiber, CO2, or UV lasers, laser marking systems directly imprint surfaces with unparalleled precision and permanence. The process engraves, etches, or modifies the substrate by focusing a concentrated light beam, ensuring lasting impressions that do not fade over time like ink or dyes. Modern laser marking is highly automated and ideal for applications requiring barcodes, QR codes, serial numbers, logos, and intricate graphics across metals, plastics, glass, ceramics, and more.
How Does Laser Marking Work?
The laser, utilizing light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation, targets a surface directly. Through interaction with the material, the laser alters its properties, thereby causing noticeable changes to the surface appearance. The laser targets a precise section of the surface needing marking. Suitable materials encompass metals, plastics, foils, films, paints, ceramics, composites, and more. Marking techniques range from annealing (heat-induced color change), staining, foaming (for plastics), engraving (material removal), to ablation and removal of coatings. Laser marking is contactless, making it a preferred solution for sensitive, fragile, or sterile products.
Types of Laser Marking Machines
Laser marking is achieved using specialized machines designed for the purpose. These machines utilize specific wavelengths of laser light tailored to different materials for effective marking. Understanding the main types of industrial laser marking systems helps you choose the optimal solution for your application:
- Fiber laser marking machines: Employing 1090-nanometer infrared lasers, fiber laser markers are ideal for marking metals and metal products such as steel, aluminum, brass, and titanium. Their infrared wavelength allows them to penetrate opaque surfaces, making them effective for annealing, engraving, and deep marking on automotive parts, electronic devices, and aerospace components. Fiber lasers are also efficient, low-maintenance, and offer high throughput for industrial environments.
- UV laser marking machines: Utilizing ultraviolet rays at a precise wavelength of 355 nm, UV laser systems enable cold marking applications. Their high absorption rate makes them suitable for materials sensitive to heat such as plastics, medical devices, silicon wafers, glass, and reflective metals like gold and copper. UV laser marking produces high-contrast, micro-fine marks without damaging the substrate, making it invaluable in microelectronics, medical device, and pharmaceutical industries.
- CO2 laser marking machines: Operating with a wavelength system ten times longer than conventional lasers, CO2 lasers are best for marking paper, wood, resins, rubbers, acrylics, and transparent materials such as glass and certain plastics. Their versatility makes them popular in packaging, beverage, textile, and signage industries for high-speed, large-area marking and engraving.
Looking for a comparison of laser marking technologies? Which laser marking system is best for your material or industry? Explore our detailed guides or connect with a marking machinery specialist for tailored recommendations.
Advantages of Laser Marking
Laser marking offers numerous benefits for industrial and commercial applications:
- Permanence and durability: Laser marks are highly resistant to abrasion, chemicals, and environmental exposure, ensuring traceability and compliance over the product’s lifecycle.
- Precision and versatility: Capable of producing high-resolution marks, fine text, barcodes, and graphics on a vast range of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites.
- Traceability and anti-counterfeiting: Unique identification, serialization, and data matrix codes enable product tracking, recall management, and authentication, helping combat counterfeiting and ensure supply chain integrity.
- Minimal waste and environmental impact: Laser marking is a non-contact, inkless process that does not require consumables, reducing operating costs and environmental footprint.
- Automation-ready and integration: Modern laser systems are easily integrated into automated production lines, ERP systems, and vision inspection platforms, increasing productivity and reducing human error.
- Low maintenance: With few moving parts and no consumables, laser marking systems offer lower maintenance costs and higher uptime compared to traditional marking methods.
Still weighing your options? How does laser marking compare to inkjet, mechanical engraving, or chemical etching? Read our in-depth comparisons or request a demo from leading manufacturers.
Laser Marking Applications
Laser technology has versatile applications, some of which are as follows:
- Jewelry and precious metals: Metals employed in jewelry possess delicate properties necessitating intricate designs, susceptible to damage from excessive heat. Laser marking emerges as the optimal solution in the goldsmith industry, offering cold marking capabilities for gold, silver, and platinum without compromising material integrity. This method enables swift and precise labeling of numerous products, ensuring compliance with industry regulations for long-term traceability and authenticity.
- Automotive and aerospace: Laser marking is used for VIN codes, part numbers, and safety critical information on engine blocks, gears, and instrumentation, supporting traceability and warranty management.
- Medical devices and surgical instruments: Permanent, sterile markings such as UDI (Unique Device Identification), batch numbers, and logos are required for compliance with FDA and EU MDR regulations. Laser marking delivers biocompatible, high-contrast, and corrosion-resistant marks on stainless steel, titanium, and plastics.
- Electronics and semiconductors: Laser systems mark PCBs, microchips, connectors, and housings with data matrix codes, logos, and production information, facilitating component tracking and anti-counterfeiting.
- Packaging and consumer goods: Use laser marking for expiration dates, lot codes, barcodes, and graphics on cartons, bottles, and flexible packaging, ensuring legibility and compliance with industry standards.
- Photoengraving and decorative marking: Finely tuned laser markers can make micro-cuts, slicing surfaces just a few millimeters thick with exceptional precision. Additionally, they enable photoengraving on metals, glass, and ceramics, accurately reproducing images or photographs onto the desired surface for personalization or artistic effects.
Curious about industry-specific marking solutions? What are the top marking methods for medical, automotive, or electronics manufacturing? Explore our industry application pages for expert insights.
Marking Machinery Equipment Components
Marking machinery typically incorporates various components, drawing from a common set of options. These machines often utilize specialized tools such as scribers, press stamps, steel stamps, rubber stamps, printing plates, and other marking instruments. Understanding the function and selection of these components is crucial for achieving consistent, high-quality marks in your production environment.
- Scribers: Integral parts of machinery designed to imprint marks onto materials. They are typically slender in shape and can be composed of durable materials such as metal, diamond, or lasers for fine, precise marking on hard surfaces.
- Press stamps: Integral components of stamping machines, press stamps operate using either hydraulic or pneumatic power sources. They apply force to create indented or embossed marks, ideal for metal tags and plates.
- Steel stamps: Used for low production volumes, steel stamps imprint products by striking or pressing into a material, creating permanent indentations for identification, batch numbers, or logos. They are widely used in hand stamping and low-volume part marking.
- Hot rubber stamps: Closely resembling steel stamps, hot rubber stamps are crafted from heat-resistant rubber or silicone rather than steel plates. They are ideal for marking plastics, textiles, and packaging materials with logos or lot codes.
- Printing plates: Used in pad printing and offset printing, these plates transfer ink or paint to a pad or directly onto the product surface for high-resolution, multi-color marks.
Benefits of Marking Machinery
Marking machinery offers many benefits for manufacturers and businesses seeking efficiency, compliance, and quality:
- High speed and throughput: Automated marking machines operate much faster than manual methods, supporting high-volume production lines and reducing operational bottlenecks.
- Accuracy and repeatability: CNC and computer-controlled marking systems ensure consistent placement, depth, and legibility of marks, minimizing defects and rework.
- Quality assurance and traceability: Marking enables efficient tracking of parts throughout manufacturing processes, supporting quality control, recalls, and regulatory compliance.
- Versatility and adaptability: Modern marking equipment can be customized or reprogrammed to handle different products, materials, and marking formats, making them suitable for diverse production needs.
- Reduced labor and operating costs: Automation reduces manual labor requirements and operator errors, streamlining workflow and lowering total cost of ownership.
- Enhanced brand value: Permanent, high-quality marks reinforce brand identity and product authenticity, building trust with customers and end-users.
Not sure which marking solution delivers the best ROI for your business? What are the cost and performance comparisons for laser, inkjet, and mechanical marking machines? Check out our buying guides or get in touch for a personalized consultation.
Marking Machinery Design and Customization
When designing marking machinery, manufacturers must consider several application aspects to ensure optimal performance and compliance. Key factors include:
- The types of markings required (deep cuts, delicate decorations, serial numbers, barcodes, or precise cuts for electronics)
- The materials and surfaces to be marked (e.g., metal, plastic, glass, ceramics, wood)
- The required production speed and volume
- System size and footprint relative to available factory space
- Integration with existing automation, MES, or quality inspection systems
- Compliance with industry standards, labeling regulations, and environmental directives
These application details assist in determining the type of marking system to design and the appropriate marking tools to install. For instance, if precise mark placement and alignment are crucial, or if marking involves handling a high volume of products, a comprehensive marking machine system is likely to be developed to meet those requirements, often with vision inspection, automation, and data logging features.
Before determining which marking machine is appropriate for an application, consider the cost of spare parts, maintenance complexity, machine footprint, and the integration difficulty with other production equipment already in place. Evaluating these factors early helps prevent costly retrofits or production delays.
Looking for advice on system integration or custom solutions? How do you automate marking in a smart factory or Industry 4.0 environment? Browse our solutions pages or consult with an engineering expert for tailored recommendations.
Marking Machinery Safety and Compliance Standards
Markings play a crucial role in product safety, traceability, and regulatory compliance. Acquiring marking machinery that meets rigorous quality standards is essential for your operations and reputation. It’s equally vital to maintain this equipment to ensure it consistently meets these high standards.
In the United States, all marking machinery must comply with OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) safety standards. Internationally, adherence to directives and guidelines from organizations like ISO (International Organization for Standardization) and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) is crucial for your marking equipment. Moreover, machinery destined for use in the European Union or for producing goods bound for the EU must bear the CE mark. This mark serves as a quality assurance stamp, indicating that your equipment has passed rigorous testing according to official conformity assessment procedures, and meets all EU environmental, health, and safety directives.
Ensuring your marking equipment and processes meet industry and governmental standards not only prevents costly fines and recalls but also builds trust with your customers and partners. What certifications and documentation are required for marking machinery in your industry? Review our compliance resources or speak with a regulatory advisor to ensure full adherence.
Choosing the Right Marking Machinery Manufacturer
If you’re in the market for industrial marking solutions, consulting with a specialist in this field is essential. To assist you in making an informed decision, we’ve compiled a list featuring the leading manufacturers of marking machinery available today. While we endorse all the manufacturers listed, it’s important to recognize that each offers unique strengths, specialized technologies, and industry expertise.
To identify the best fit for your marking needs:
- Review manufacturer profiles, considering their experience with your target materials and applications
- Assess which companies offer solutions that align with your technical requirements and budget
- Request case studies, references, or demonstrations to evaluate performance and customer support
- Narrow down your choices to three or four top contenders, then reach out to each one to discuss your specific application requirements in detail
- Leave no detail unexplored: cover budget considerations, integration needs, production deadlines, part sizes, delivery requirements, and technical specifications
- Compare notes after your consultations and determine which manufacturer best meets your criteria for quality, service, and long-term partnership
Ready to take the next step? What questions should you ask a marking machinery supplier before making a purchase? Download our free buyer’s checklist or connect with our team for personalized recommendations and vendor introductions.
For more information, in-depth guides, and to explore a comprehensive range of marking machinery solutions for your industry, browse our directory of top marking machinery manufacturers or use our search tool to find the right partner for your project.
What types of materials can marking machinery process?
Marking machinery is highly versatile and can process a wide variety of materials, including metal, paper, plastic, wood, leather, glass, fabric, and textiles. Specialized machines allow for effective marking on both industrial and creative products.
How does laser marking work?
Laser marking uses concentrated beams of light to modify the surface of a material. The process alters the material’s properties—through techniques like engraving, annealing, foaming, staining, or ablation—without physical contact. Suitable for metals, plastics, glass, ceramics, and more, laser marking produces highly precise, lasting marks.
What are the main types of marking machinery?
Common types of marking machinery include press markers, dot peen machines, nameplate markers, embossing machines, engraving machines, roll markers, hot stamp presses, hand stamping tools, numbering machines, printing machines (like inkjet and pad printers), chemical etching equipment, plasma etchers, and laser marking systems. Each type serves distinct marking needs and materials.
What are the advantages of using laser marking over traditional marking methods?
Laser marking offers exceptional permanence, precision, and versatility, producing marks resistant to abrasion and chemicals. It’s a non-contact, inkless process that reduces waste and is suitable for automation. Laser markers are low-maintenance, easily integrated into production lines, and deliver high-speed, consistent results across a range of materials.
Which industries commonly use marking machinery?
Marking machinery is essential in industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical device manufacturing, packaging, jewelry production, and more. It is used for compliance, product identification, traceability, quality control, branding, and decorative applications.
What standards and certifications should marking machinery comply with?
Marking machinery must meet safety and quality standards such as OSHA (for the U.S.), ISO, IEC, and the CE mark (for Europe). Compliance ensures equipment meets stringent environmental, health, and safety directives—helping avoid fines, recalls, and ensuring customer trust.
How should I select the right marking machinery for my application?
To select the right marking machinery, consider your material type, desired marking method, production speed, marking durability, compliance requirements, integration needs, and budget. Consulting manufacturer profiles, reviewing case studies, and requesting demonstrations will help determine the optimal solution for your specific needs.




 Cardboard Tubes
Cardboard Tubes Carrying Cases
Carrying Cases Contract Packaging
Contract Packaging Corrugated Boxes
Corrugated Boxes Dot Peening Machines
Dot Peening Machines Labeling Machinery
Labeling Machinery Marking Machinery
Marking Machinery Packaging Equipment
Packaging Equipment Palletizers
Palletizers Plastic Bags
Plastic Bags Sewing Contractors
Sewing Contractors Tape Suppliers
Tape Suppliers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services